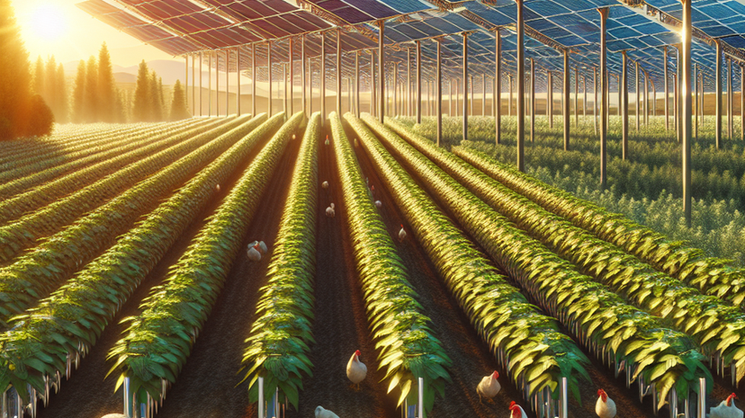
The realm of sustainable energy and food production is going through a revolution with agrivoltaics. This approach combines large-scale solar farming with optimized agricultural yields, effectively using solar power while creating a harmonious coexistence between solar panels and crops. In this article, we explore the world of agrivoltaics and witness its transformative impact on agriculture.
Imagine a vast farm with solar panels shining under the sun. But instead of empty land, there’s life beneath these panels. Animals like sheep, chickens, and geese roam freely, providing natural fertilization and pest control, benefiting from the shade and shelter offered by the panels. This concept, known as agrivoltaics, optimizes land use, enhances biodiversity, and promotes sustainable farming.
One advantage of agrivoltaics is its capacity to support farming and solar panels together, benefiting both. Animals help maintain the solar installations, maximizing land use and promoting biodiversity. This benefits the environment and generates additional income for farmers, ensuring their economic viability.
Experts like Matt Ferrell and John Smilie have dedicated their efforts to educating others about agrivoltaics. Ferrell’s video, “Solar Panels Plus Farming Agrivoltaics Explained,” explains this farming technique and its potential. Similarly, Smilie shares his research findings, enlightening farmers and policymakers about the benefits and implementation of agrivoltaics.
Agrivoltaics also uses bifacial solar panels, generating more power during morning and evening hours, complementing traditional solar panels. These panels cool the land beneath them, preserving moisture, improving water efficiency, and increasing crop yields. Farms in Europe have even started mounting bifacial modules vertically on their solar panels to reduce wind erosion and enhance moisture retention, further improving solar farming.
Despite its advantages, agrivoltaics faces challenges in widespread implementation due to the “not-in-my-backyard” effect, bureaucracy, and market concerns. However, by emphasizing economic benefits and environmental advantages, communities can embrace this innovative approach to energy and food production.
The impact of agrivoltaics on crop yields is of great interest. Shade-tolerant plants thrive under solar panels, benefiting from reduced sunlight exposure. Yields for sun-loving crops may vary depending on climate conditions. Nevertheless, agrivoltaic fields have shown resilience, outperforming non-solar fields, especially during dry and hot years.
Traditional farming often dedicates large areas of land to energy production using crops like corn and soy for biofuels. Solar farming, on the other hand, offers much higher energy outputs per acre, providing an alternative to conventional farming practices. By harnessing renewable energy, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change impacts.
Agrivoltaics represents a promising future for the agricultural and renewable energy sectors. This practice combines the power of the sun with sustainable farming techniques, benefiting farmers, consumers, and the environment. As we continue to explore and refine agrivoltaics, we pave the way for a greener and more resilient future.